Meta CEO: AI Could Replace Mid-Level Developers
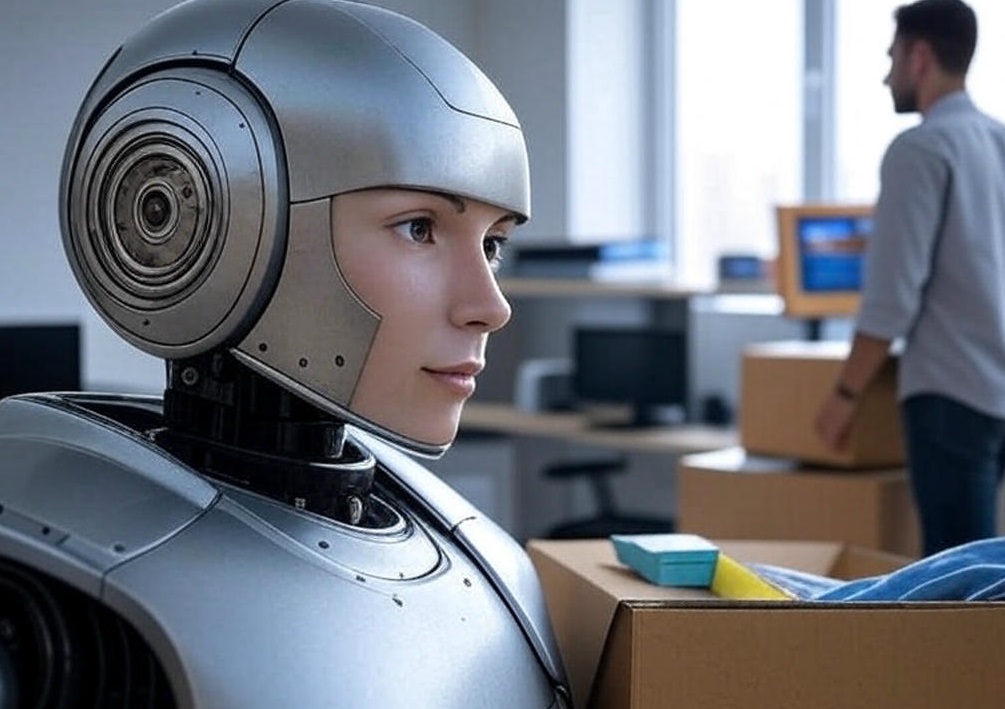
Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg made a bold statement, predicting that artificial intelligence could soon replace mid-level developers. In an interview on the Joe Rogan Experience podcast, he explained that Meta and other leading tech companies are actively developing AI systems capable of coding at the level of mid-tier engineers.
AI and the Future of Programming
Zuckerberg noted that AI’s capabilities in programming are rapidly evolving, and tech giants like Meta, Google, and Microsoft are already integrating AI to generate code. These systems can not only handle basic coding tasks but also develop complex projects that previously required the collaboration of several developers. However, there are certain limitations — such as AI “hallucinations,” where the system produces incorrect or illogical results.
The Impact of AI on the Tech Industry
Other leaders in the tech space are also betting on AI’s potential. For example, Y Combinator CEO Garry Tan emphasized that in the future, small teams could leverage large language models to build apps that once needed dozens of developers.
Forecasts from Other Industry Leaders
Tobi Lütke, CEO of Shopify, stated that companies might require managers to justify new hires if AI can handle the task more efficiently.
Dario Amodei, co-founder of Anthropic, predicts that AI will be capable of writing nearly all code within a year.
Sundar Pichai, CEO of Google, revealed that over 25% of the company’s new code is generated by AI, significantly boosting productivity.
Risks of Overreliance on AI in Programming
However, experts like Cambridge University AI researcher Harry Law warn about the dangers of overreliance on AI in software development. He believes it could complicate learning, debugging, and may introduce vulnerabilities without proper code review.
AI in Programming: Future, Opportunity, or Threat?
Despite the remarkable progress, AI in programming still raises concerns. The ability to generate code without human input opens new frontiers but demands rigorous oversight and monitoring to avoid errors that could impact the security and reliability of software systems.